Plant materials and applied treatments
The original plant materials were obtained from the seeds of the third-generation seed-orchard of Chinese fir species in Youxi National Farm, Fujian province. The seeds of each available genotype were planted in pots and the seedlings growth were evaluated. One superior Chinese fir clone (No. 7–14, propagated asexually) was chosen as the study material. Besides its growth rate, the No. 7–14 family has strong drought resistance and nitrogen absorption ability42. The average seedling height was 38.5 cm. Plantlets were grown using a water cultivation method under controlled conditions (16:8 h light: dark regime, 120 μmol m−2 s−1 photon flux; at 25 °C and 60% RH) in a growth chamber (LT-ACC400, China).
The basic nutrient solution was controlled using a modified Hoagland nutrient solution that contained K2SO4 (0.41 g L−1), Mg2SO4·7H2O (0.49 g L−1), KH2PO4 (0.136 g L−1); H3BO3 (0.286 g L−1), H2MoO4 (0.0623 g L−1), MnCl2·4H2O (0.181 g L−1), CuSO4·5H2O (0.008 g L−1), ZnSO4·7H2O (0.022 g L−1); ferric salts, FeSO4·7H2O (0.278 g L−1), and EDTA-Na2 (0.373 g L−1). Three nitrogen sources were used to provide 4.571 mM: NO3−N from Ca(NO3)2 at 0.3748 g L−1, NH4+-N from (NH4)2SO4 at 0.3016 g L−1, and the combination treatment using NO3−N and NH4+-N from Ca(NO3)2 at 0.1874 g L−1 and (NH4)2SO4 at 0.1508 g L−1. We then added nitrification inhibitor (0.01 mM Dicyandiamide, DCD) to each of these nutrient solutions. In total, eight treatments were applied: CK (normal water + basic nutrient solution without nitrogen), N (NO3−N only), A (NH4+-N only), AN (NO3−N + NH4+-N), P (10% PEG), NP (NO3−N + 10% PEG), AP (NH4+-N + 10% PEG), and ANP (NO3−N + NH4+-N + 10% PEG). After acclimation, plantlets were divided into eight treatment groups; each with three replicates.
Antioxidant enzyme activity and lipid peroxidation determination
Enzyme liquid extraction: Fresh one-year needles (~0.2 g) were homogenized in liquid nitrogen in centrifuge tubes (5 mL) for 15 min, and then phosphate buffer (4 mL, pH = 7) was added. The homogenates were centrifuged at 10,000 g for 20 min at 4 °C. The supernatants were used to determine the antioxidant enzyme activity as described below.
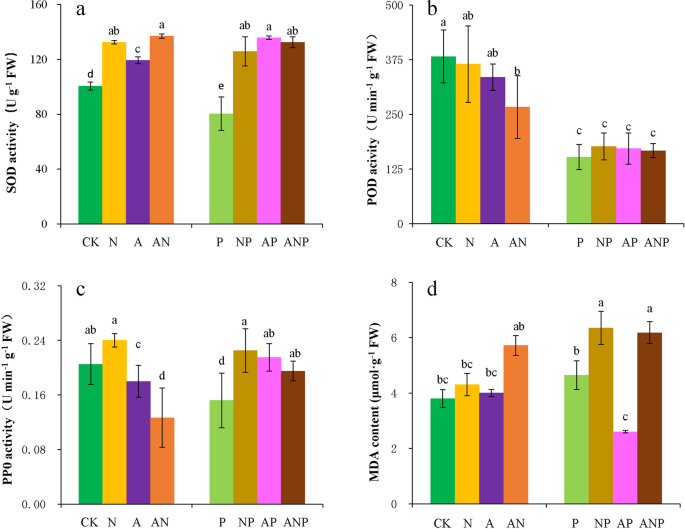
Superoxide dismutase activity (SOD; EC 1.15.1.1): SOD was determined by the inhibition of the photochemical reduction of nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) according to Costa et al.42. The reaction mixture contained 0.1 mL of enzyme extract in 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer, (pH = 7.8), 0.1 mM EDTA, 50 mM methionine, 75 μM NBT, and 20 μM riboflavin. The reaction mixtures were placed under a high intensity lamp (4000 lx) for 15 min. They were then placed in the dark to stop the reaction, and the absorbance at 560 nm was recorded (Puxi Instrument, Beijing, China). One unit of SOD was defined as the amount of enzymes required to produce 50% inhibition of NBT reduction.
Peroxidase activity (POD; EC 1.11.1.7): the POD activity was determined according to Ekmekca and Terzioglu43. The reaction mixture contained 2.9 mL of 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer (pH = 6.0), 1 mL of 50 mM guaiacol, 1 mL of 50 mM H2O2, and 0.1 mL of enzyme extract. Absorbance at 470 nm was recorded.
Polyphenol oxidase activity (PPO; EC 1.14.18.1): the PPO activity was determined at 420 nm in a spectrophotometer44. The reaction mixture contained 1.5 mL of 0.02 M NaSO4 solution, 5 mM substrate, and 1.5 mL of enzyme extract. After the reaction was completed, absorbance at 420 nm was recorded every 1 min. In total, five absorbance readings were recorded. One unit of enzyme activity was defined as the amount of enzymes required to cause a rate of change of 0.001 absorption unites per min at 420 nm.
Lipid peroxidation determination: Lipid peroxidation was estimated by measurement of malondialdehyde (MDA, a product of lipid peroxidation) using thiobarbituric acid (TBA) according to Hasanuzzaman et al.45. The reaction mixture was homogenized in a centrifuge tube containing 2.5 mL of 0.5% TBA and 1.5 mL of enzyme extract. The mixture was placed in boiling water for 15 min and centrifuged for 10 min at 4000 rpm after cooling. The supernatant was measured and absorbance recorded at 450 nm, 532 nm, and 600 nm. Results were expressed as μmol g-1 on a fresh weight (FW) basis.
Osmotic adjustment substances
Enzyme liquid extraction: Chinese fir needle samples (0.1 g) were ground in liquid nitrogen and dissolved in 0.9 mL phosphate buffer (pH = 7.2). The mixtures were centrifuged for 10 min at 10,000 g, and the supernatants used for determination of osmotic-adjustment substances.
Proline content: Proline was measured according to Bates et al.46. Briefly, the supernatant was mixed with acid ninhydrin with glacial acetic acid and phosphoric acid. This mixture was incubated in a boiling-water bath for 1 h. Cooling toluene was then added. After chromophore containing toluene was produced, absorbance was read at 520 nm.
Soluble sugars: Soluble sugars were determined by the anthrone method47. Reaction mixtures contained 1 mL extract, 1 mL distilled water, 0.5 mL mixed reagent (1 g anthrone + 50 mL ethyl acetate), and 5 mL H2SO4 (98%). The mixtures were heated in a boiling-water bath for 1 min. After cooling, absorbance was recorded at 630 nm.
Nitrogen metabolism
Nitrate reductase activity (EC 1.6.6.1): the NR activity was determined according to Silveira et al.41. Samples (0.2 g) of 7 mm length were placed in vials of ice – cold incubation medium, consisting of 100 mM K-phosphate buffer (pH 7.5), 50 mM KNO3, and 1% (v/v) isopropanol. Tissues were vacuum-infiltrated for 2 min at -67 kPa, and then incubated in water in the dark for 30 min at 30 °C. After incubation, the concentration of nitrite released into the medium was determined by measuring absorbance at 540 nm.
GS activity (EC 6.3.1.2): Enzyme liquid extraction was performed following the method for osmotic adjustment substances. GS activity was determined by the hydroxamate biosynthetic method with the following reaction mixture: Tris-HCl buffer (pH = 7.0), 200 μL 300 mM sodium glutamate (pH = 7.0), 200 μL 30 mM ATP (pH = 7.0), 200 μL 500 mM MgSO4, and 200 μL 1000 mM hydroxylamine hydrochloride neutralized with 1000 mM HCl and 500 μL of enzyme extract. The mixtures were incubated at 30 °C for 30 min. After brown complex formation, absorbance was recorded at 540 nm.
GOGAT activity (EC 1.4.7.1): The mixture contained 25 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.6), 0.4 mL 20 mM L-glutamine, 0.05 mL 0.1 M 2-oxoglutarate, 0.1 mL 10 mM KCl, 0.2 mL 3 mM NADH, and 0.5 mL of enzyme extract. Absorbance was read at 340 nm.
Statistical analysis
One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed to determine significant treatment effects, followed by the least significant difference test (LSD) for separate the means. The data are means ± SE. Differences at P ≤ 0.05 were regarded as significant. The software SPSS Statistical Package (SPSS 12.0, SPSS Ins., IL, USA) was used to perform the statistical analysis.
Source: Ecology - nature.com


