Fendorf, S., Michael, H. A. & van Geen, A. Spatial and temporal variations of groundwater arsenic in South and Southeast Asia. Science 328, 1123–1127 (2010).
Winkel, L. H. et al. Arsenic pollution of groundwater in Vietnam exacerbated by deep aquifer exploitation for more than a century. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 108, 1246–1251 (2011).
Postma, D. et al. Groundwater arsenic concentrations in Vietnam controlled by sediment age. Nat. Geosci. 5, 656–661 (2012).
Berg, M. et al. Hydrological and sedimentary controls leading to arsenic contamination of groundwater in the Hanoi area, Vietnam: the impact of iron–arsenic ratios, peat, river bank deposits, and excessive groundwater abstraction. Chem. Geol. 249, 91–112 (2008).
Radloff, K. et al. Reversible adsorption and flushing of arsenic in a shallow, Holocene aquifer of Bangladesh. Appl. Geochem. 77, 142–157 (2017).
Neumann, R. B. et al. Anthropogenic influences on groundwater arsenic concentrations in Bangladesh. Nat. Geosci. 3, 46–52 (2010).
van Geen, A. et al. Retardation of arsenic transport through a Pleistocene aquifer. Nature 501, 204–207 (2013).
Khan, M. R. et al. Megacity pumping and preferential flow threaten groundwater quality. Nat. Commun. 7, 12833 (2016).
Michael, H. A. & Khan, M. R. Impacts of physical and chemical aquifer heterogeneity on basin-scale solute transport: vulnerability of deep groundwater to arsenic contamination in Bangladesh. Adv. Water Resour. 98, 147–158 (2016).
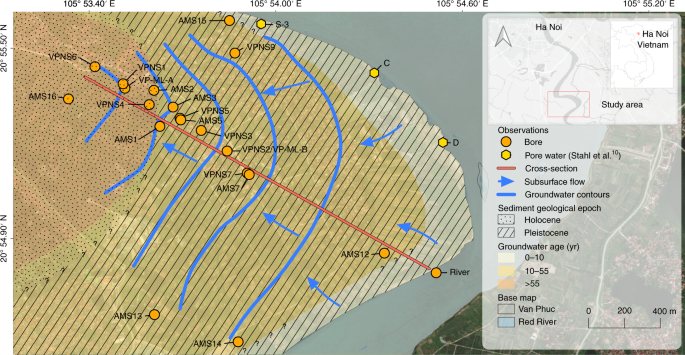
Stahl, M. O. et al. River bank geomorphology controls groundwater arsenic concentrations in aquifers adjacent to the Red River, Hanoi Vietnam. Water Resour. Res. 52, 6321–6334 (2016).
McArthur, J., Ravenscroft, P., Safiulla, S. & Thirlwall, M. Arsenic in groundwater: testing pollution mechanisms for sedimentary aquifers in Bangladesh. Water Resour. Res. 37, 109–117 (2001).
McArthur, J. et al. Natural organic matter in sedimentary basins and its relation to arsenic in anoxic ground water: the example of West Bengal and its worldwide implications. Appl. Geochem. 19, 1255–1293 (2004).
Meharg, A. A. et al. Codeposition of organic carbon and arsenic in Bengal Delta aquifers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 40, 4928–4935 (2006).
Postma, D. et al. Arsenic in groundwater of the Red River floodplain, Vietnam: controlling geochemical processes and reactive transport modeling. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 71, 5054–5071 (2007).
Polizzotto, M. L., Kocar, B. D., Benner, S. G., Sampson, M. & Fendorf, S. Near-surface wetland sediments as a source of arsenic release to ground water in Asia. Nature 454, 505–509 (2008).
Stuckey, J. W., Schaefer, M. V., Kocar, B. D., Benner, S. G. & Fendorf, S. Arsenic release metabolically limited to permanently water-saturated soil in Mekong Delta. Nat. Geosci. 9, 70–76 (2016).
Berg, M. et al. Arsenic contamination of groundwater and drinking water in Vietnam: a human health threat. Environ. Sci. Technol. 35, 2621–2626 (2001).
Harvey, C. F. et al. Arsenic mobility and groundwater extraction in Bangladesh. Science 298, 1602–1606 (2002).
Horneman, A. et al. Decoupling of As and Fe release to Bangladesh groundwater under reducing conditions. Part 1: Evidence from sediment profiles. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 68, 3459–3473 (2004).
Islam, F. S. et al. Role of metal-reducing bacteria in arsenic release from Bengal delta sediments. Nature 430, 68–71 (2004).
Eiche, E. Arsenic Mobilization Processes in the Red River Delta, Vietnam: Towards a Better Understanding of the Patchy Distribution of Dissolved Arsenic in Alluvial Deposits (Karlsruher Mineralogische und Geochemische Hefte 37, KIT Scientific, 2009).
Frei, F. Groundwater Dynamics and Arsenic Mobilization near Hanoi (Vietnam) Assessed Using Noble Gases and Tritium Diploma Thesis, ETH Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Department of Environmental Sciences (2007).
Eiche, E. et al. Origin and availability of organic matter leading to arsenic mobilisation in aquifers of the Red River Delta, Vietnam. Appl. Geochem. 77, 184–193 (2017).
Postma, D. et al. Mobilization of arsenic and iron from Red River floodplain sediments, Vietnam. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 74, 3367–3381 (2010).
Postma, D. et al. Fate of arsenic during Red River water infiltration into aquifers beneath Hanoi, Vietnam. Environ. Sci. Technol. 51, 838–845 (2017).
Larsen, F. et al. Controlling geological and hydrogeological processes in an arsenic contaminated aquifer on the Red River flood plain, Vietnam. Appl. Geochem. 23, 3099–3115 (2008).
McClain, M. E. et al. Biogeochemical hot spots and hot moments at the interface of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Ecosystems 6, 301–312 (2003).
Cheng, F. Y. & Basu, N. B. Biogeochemical hotspots: role of small water bodies in landscape nutrient processing. Water Resour. Res. 53, 5038–5056 (2017).
Hedin, L. O. et al. Thermodynamic constraints on nitrogen transformations and other biogeochemical processes at soil–stream interfaces. Ecology 79, 684–703 (1998).
Kocar, B. D. & Fendorf, S. in Interdisciplinary Studies on Environmental Chemistry—Environmental Pollution and Ecotoxicology (eds Kawaguchi, M. et al.) 117–124 (TERRAPUB, 2012).
Rathi, B., Neidhardt, H., Berg, M., Siade, A. & Prommer, H. Processes governing arsenic retardation on Pleistocene sediments: adsorption experiments and model‐based analysis. Water Resour. Res. 53, 4344–4360 (2017).
Eiche, E. et al. Geochemical processes underlying a sharp contrast in groundwater arsenic concentrations in a village on the Red River delta, Vietnam. Appl. Geochem. 23, 3143–3154 (2008).
van Geen, A. et al. Comparison of arsenic concentrations in simultaneously-collected groundwater and aquifer particles from Bangladesh, India, Vietnam, and Nepal. Appl. Geochem. 23, 3244–3251 (2008).
Neidhardt, H. et al. Insights into arsenic retention dynamics of Pleistocene aquifer sediments by in situ sorption experiments. Water Res. 129, 123–132 (2018).
van Geen, A. et al. Spatial variability of arsenic in 6000 tube wells in a 250 km2 area of Bangladesh. Water Resour. Res. 39, 1140 (2003).
McArthur, J. et al. How paleosols influence groundwater flow and arsenic pollution: a model from the Bengal Basin and its worldwide implication. Water Resour. Res. 44, W11411 (2008).
Harbaugh, A. W. MODFLOW-2005, the US Geological Survey Modular Ground-water Model: The Ground-water Flow Process (US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey, 2005).
Prommer, H., Barry, D. A. & Zheng, C. MODFLOW/MT3DMS-based reactive multicomponent transport modeling. Ground Water 41, 247–257 (2003).
Zheng, C. & Wang, P. P. MT3DMS: A Modular Three-dimensional Multispecies Transport Model for Simulation of Advection, Dispersion, and Chemical Reactions of Contaminants in Groundwater Systems; Documentation and User’s Guide (U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Document, 1999).
Parkhurst, D. L. & Appelo, C. User’s Guide to PHREEQC (Version 2): A Computer Program for Speciation, Batch-Reaction, One-Dimensional Transport, and Inverse Geochemical Calculations Report No. 99-4259 (USGS, 1999).
Welter, D. E., White, J. T., Hunt, R. J. & Doherty, J. E. Approaches in Highly Parameterized Inversion—PEST++ Version 3, a Parameter ESTimation and Uncertainty Analysis Software Suite Optimized for Large Environmental Models Report No. 2328-7055 (USGS, 2015).
Postma, D. & Jakobsen, R. Redox zonation: equilibrium constraints on the Fe(iii)/SO4-reduction interface. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 60, 3169–3175 (1996).
Prommer, H., Tuxen, N. & Bjerg, P. L. Fringe-controlled natural attenuation of phenoxy acids in a landfill plume: integration of field-scale processes by reactive transport modeling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 40, 4732–4738 (2006).
Sharma, L., Greskowiak, J., Ray, C., Eckert, P. & Prommer, H. Elucidating temperature effects on seasonal variations of biogeochemical turnover rates during riverbank filtration. J. Hydrol. 428, 104–115 (2012).
Rawson, J. et al. Quantifying reactive transport processes governing arsenic mobility after injection of reactive organic carbon into a Bengal Delta aquifer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 51, 8471–8480 (2017).
Schwertmann, U. Solubility and dissolution of iron oxides. Plant Soil 130, 1–25 (1991).
Appelo, C. A. J., Van der Weiden, M. J. J., Tournassat, C. & Charlet, L. Surface complexation of ferrous iron and carbonate on ferrihydrite and the mobilization of arsenic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 36, 3096–3103 (2002).
Dzombak, D. A. & Morel, F. M. Surface Complexation Modeling: Hydrous Ferric Oxide (John Wiley & Sons, 1990).
Swedlund, P. J. & Webster, J. G. Adsorption and polymerisation of silicic acid on ferrihydrite, and its effect on arsenic adsorption. Water Res. 33, 3413–3422 (1999).
Source: Resources - nature.com


