Moran NA. Symbiosis as an adaptive process and source of phenotypic complexity. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2007;104:8627–33.
Rubin-Blum M, Antony CP, Sayavedra L, Martínez-Pérez C, Birgel D, Peckmann J, et al. Fueled by methane: deep-sea sponges from asphalt seeps gain their nutrition from methane-oxidizing symbionts. ISME J. 2019;13:1209–25.
Muscatine L, Cernichiari E. Assimilation of photosynthetic products of zooxanthellae by a reef coral. Biol Bull. 1969;137:506–23.
Baker DM, Freeman CJ, Knowlton N, Thacker RW, Kim K, Fogel ML. Productivity links morphology, symbiont specificity and bleaching in the evolution of Caribbean octocoral symbioses. ISME J. 2015;9:2620–9.
Pollock FJ, McMinds R, Smith S, Bourne DG, Willis BL, Medina M, et al. Coral-associated bacteria demonstrate phylosymbiosis and cophylogeny. Nat Commun. 2018;9:1–13.
Freeman CJ, Thacker RW, Baker DM, Fogel ML. Quality or quantity: is nutrient transfer driven more by symbiont identity and productivity than by symbiont abundance? ISME J. 2013;7:1116–25.
Freeman CJ, Stoner EW, Easson CG, Matterson KO, Baker DM. Symbiont carbon and nitrogen assimilation in the Cassiopea–Symbiodinium mutualism. Mar Ecol Prog Ser. 2016;544:281–6.
Maldonado M, Ribes M, van Duyl FC. Nutrient fluxes through sponges: biology, budgets, and ecological implications. Adv Mar Biol. 2012;62:113–82.
Morganti T, Coma R, Yahel G, Ribes M. Trophic niche separation that facilitates co-existence of high and low microbial abundance sponges is revealed by in situ study of carbon and nitrogen fluxes. Limnol Oceanogr. 2017;62:1963–83.
McMurray SE, Stubler AD, Erwin PM, Finelli CM, Pawlik JR. A test of the sponge-loop hypothesis for emergent Caribbean reef sponges. Mar Ecol Prog Ser. 2018;588:1–14.
Moya A, Peretó J, Gil R, Latorre A. Learning how to live together: genomic insights into prokaryote–animal symbioses. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:218–29.
Thomas T, Moitinho-Silva L, Lurgi M, Björk JR, Easson C, Astudillo-García C, et al. Diversity, structure and convergent evolution of the global sponge microbiome. Nat Commun. 2016;7:1–12.
Wilkinson CR. Interocean differences in size and nutrition of coral reef sponge populations. Science. 1987;236:1654–7.
Erwin PM, Thacker RW. Incidence and identity of photosynthetic symbionts in Caribbean coral reef sponge assemblages. J Mar Biol Assoc UK. 2007;87:1683–92.
Southwell MW, Popp BN, Martens CS. Nitrification controls on fluxes and isotopic composition of nitrate from Florida Keys sponges. Mar Chem. 2008;108:96–108.
Zhang F, Vicente J, Hill RT. Temporal changes in the diazotrophic bacterial communities associated with caribbean sponges Ircinia strobilina and Mycale laxissima. Front Microbiol. 2014;5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00561.
Rädecker N, Pogoreutz C, Voolstra CR, Wiedenmann J, Wild C. Nitrogen cycling in corals: the key to understanding holobiont functioning? Trends Microbiol. 2015;23:490–7.
McMurray SE, Johnson ZI, Hunt DE, Pawlik JR, Finelli CM. Selective feeding by the giant barrel sponge enhances foraging efficiency. Limnol Oceanogr. 2016;61:1271–86.
Fiore CL, Freeman CJ, Kujawinski EB. Sponge exhalent seawater contains a unique chemical profile of dissolved organic matter. PeerJ. 2017;5:e2870.
Zhang F, Jonas L, Lin H, Hill RT. Microbially mediated nutrient cycles in marine sponges. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2019;95. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiz155.
Webster NS, Thomas T. The sponge hologenome. MBio. 2016;7. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00135-16.
Pita L, Rix L, Slaby BM, Franke A, Hentschel U. The sponge holobiont in a changing ocean: from microbes to ecosystems. Microbiome. 2018;6:46.
Vacelet J, Donadey C. Electron microscope study of the association between some sponges and bacteria. J Exp Mar Bio Ecol. 1977;30:301–14.
Weisz JB, Hentschel U, Lindquist N, Martens CS. Linking abundance and diversity of sponge-associated microbial communities to metabolic differences in host sponges. Mar Biol. 2007;152:475–83.
Gloeckner V, Wehrl M, Moitinho-Silva L, Gernert C, Schupp P, Pawlik JR, et al. The HMA-LMA dichotomy revisited: an electron microscopical survey of 56 sponge species. Biol Bull. 2014;227:78–88.
Easson CG, Thacker RW. Phylogenetic signal in the community structure of host-specific microbiomes of tropical marine sponges. Front Microbiol. 2014;5:1–11.
Turon M, Cáliz J, Garate L, Casamayor EO, Uriz MJ. Showcasing the role of seawater in bacteria recruitment and microbiome stability in sponges. Sci Rep. 2018;8:15201.
Wilkinson CR. Net primary productivity in coral reef sponges. Science. 1983;219:410–2.
Wilkinson CR, Cheshire AC. Comparisons of sponge populations across the Barrier Reefs of Australia and Belize: evidence for higher productivity in the Caribbean. Mar Ecol Prog Ser. 1990;67:285–94.
Erwin PM, Thacker RW. Phototrophic nutrition and symbiont diversity of two Caribbean sponge-cyanobacteria symbioses. Mar Ecol Prog Ser. 2008;362:139–47.
Freeman CJ, Thacker RW. Complex interactions between marine sponges and their symbiotic microbial communities. Limnol Oceanogr. 2011;56:1577–86.
Levin SA. Community equilibria and stability, and an extension of the competitive exclusion principle. Am Nat. 1970;104:413–23.
Connell JH. Diversity in tropical rain forests and coral reefs. Science. 1978;199:1302–10.
Miloslavich P, Díaz JM, Klein E, Alvarado JJ, Díaz C, Gobin J, et al. Marine biodiversity in the caribbean: regional estimates and distribution patterns. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e11916.
Diaz C, Klaus R. Sponges: an essential component of Caribbean coral reefs. Bull Mar Sci. 2001;69:535–46.
Loh T-L, Pawlik JR. Chemical defenses and resource trade-offs structure sponge communities on Caribbean coral reefs. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014;111:4151–6.
Pawlik JR, Loh T-L, McMurray SE. A review of bottom-up vs. top-down control of sponges on Caribbean fore-reefs: what’s old, what’s new, and future directions. PeerJ. 2018;6:e4343.
Freeman CJ, Easson CG, Baker DM. Metabolic diversity and niche structure in sponges from the Miskito Cays, Honduras. PeerJ. 2014;2:e695.
Freeman CJ, Baker DM, Easson CG, Thacker RW. Shifts in sponge-microbe mutualisms across an experimental irradiance gradient. Mar Ecol Prog Ser. 2015;526:41–53.
Van Duyl FC, Mueller B, Meesters EH. Spatio–temporal variation in stable isotope signatures (δ13C and δ15N) of sponges on the Saba Bank. PeerJ. 2018;6:e5460.
Gause GF. Experimental analysis of Vito Volterra’s mathematical theory of the struggle for existence. Science. 1934;79:16–17.
Freeman CJ, Easson CG, Baker DM. Niche structure of marine sponges from temperate hard-bottom habitats within Gray’s Reef National Marine Sanctuary. J Mar Biol Assoc UK. 2016;96:559–65.
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods. 2010;7:335.
Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-Lyons D, Huntley J, Fierer N, et al. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J. 2012;6:1621–4.
Callahan BJ, McMurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson AJA, Holmes SP. DADA2: high-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods. 2016;13:581–3.
R Core Team. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2018.
Quast C, Pruesse E, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yilmaz P, Peplies J, et al. SILVA databases. Encyclopedia of metagenomics: genes, genomes and metagenomes: basics, methods, databases and tools. In: Nelson KE (ed.). Boston, MA: Springer US; 2015. pp 626–635.
Kembel SW, Cowan PD, Helmus MR, Cornwell WK, Morlon H, Ackerly DD, et al. Picante: R tools for integrating phylogenies and ecology. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:1463–4.
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Friendly M, Kindt R, Legendre P, McGlinn D, et al. Vegan: community ecology package. 2019. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan.
Hervé M. Package ‘RVAideMemoire’. 2019. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/RVAideMemoire/RVAideMemoire.pdf.
Wickham H. gglot2: elegant graphics for data analysis. New York: Springer-Verlag; 2016.
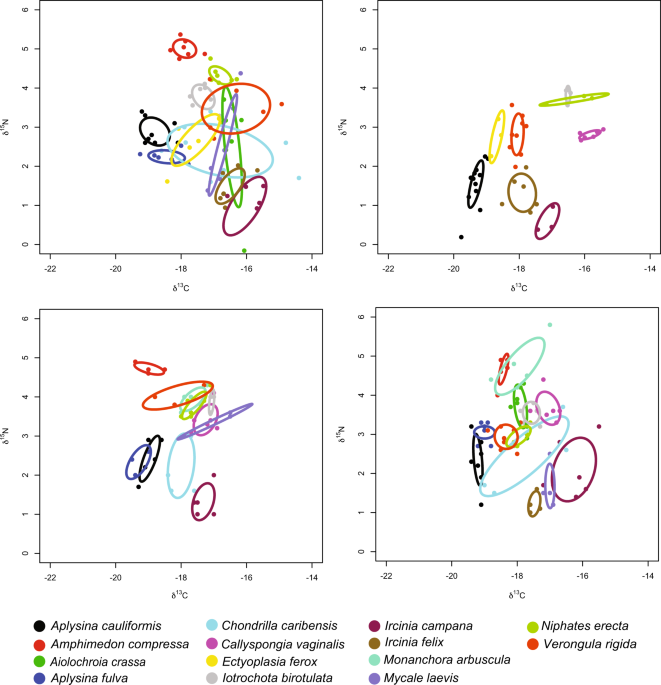
Jackson AL, Inger R, Parnell AC, Bearhop S. Comparing isotopic niche widths among and within communities: SIBER—Stable Isotope Bayesian Ellipses in R. J Anim Ecol. 2011;80:595–602.
Swanson HK, Lysy M, Power M, Stasko AD, Johnson JD, Reist JD. A new probabilistic method for quantifying n-dimensional ecological niches and niche overlap. Ecology. 2015;96:318–24.
Layman CA, Arrington DA, Montaña CG, Post DM. Can stable isotope ratios provide for community-wide measures of trophic structure? Ecology. 2007;88:42–48.
Blomberg SP, Garland JRT, Ives AR. Testing for phylogenetic signal in comparative data: behavioral traits are more labile. Evolution. 2003;57:717–45.
Easson CG. Sponge and seawater associated microbial communities from the Caribbean Sea and western Atlantic Ocean. Sequence Read Archive BioProject: PRJNA544301; BioSample Accession: SAMN11832602–SAMN11833237. 2019.
Poppell E, Weisz J, Spicer L, Massaro A, Hill A, Hill M. Sponge heterotrophic capacity and bacterial community structure in high- and low-microbial abundance sponges. Mar Ecol. 2014;35:414–24.
Schoener TW. Resource partitioning in ecological communities. Science. 1974;185:27–39.
Porter JW. Autotrophy, heterotrophy, and resource partitioning in Caribbean reef-building corals. Am Nat. 1976;110:731–42.
Jackson JBC. Adaptation and diversity of reef corals. Bioscience. 1991;41:475–82.
Corredor JE, Howarth RW, Twilley RR, Morell JM. Nitrogen cycling and anthropogenic impact in the tropical interamerican seas. Biogeochemistry. 1999;46:163–78.
Hentschel U, Piel J, Degnan SM, Taylor MW. Genomic insights into the marine sponge microbiome. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012;10:641–54.
Fan L, Reynolds D, Liu M, Stark M, Kjelleberg S, Webster NS, et al. Functional equivalence and evolutionary convergence in complex communities of microbial sponge symbionts. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2012;109:E1878–87.
Fiore CL, Baker DM, Lesser MP. Nitrogen biogeochemistry in the caribbean sponge Xestospongia muta: a source or sink of dissolved inorganic nitrogen? PLoS ONE. 2013;8:1–11.
Pawlik JR, McMurray SE, Erwin P, Zea S. A review of evidence for food limitation of sponges on Caribbean reefs. Mar Ecol Prog Ser. 2015;519:265–83.
Gantt SE, McMurray SE, Stubler AD, Finelli CM, Pawlik JR, Erwin PM. Testing the relationship between microbiome composition and flux of carbon and nutrients in Caribbean coral reef sponges. Microbiome. 2019;7:1–13.
Pawlik JR, Burkepile DE, Thurber RV. A vicious circle? Altered carbon and nutrient cycling may explain the low resilience of Caribbean coral reefs. Bioscience. 2016;66:470–6.
Friesen ML, Porter SS, Stark SC, von Wettberg EJ, Sachs JL, Martinez-Romero E. Microbially mediated plant functional traits. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst. 2011;42:23–46.
Beinart RA, Sanders JG, Faure B, Sylva SP, Lee RW, Becker EL, et al. Evidence for the role of endosymbionts in regional-scale habitat partitioning by hydrothermal vent symbioses. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2012;109:E3241–E3250.
Iglesias-Prieto R, Beltrán VH, LaJeunesse TC, Reyes-Bonilla H, Thomé PE. Different algal symbionts explain the vertical distribution of dominant reef corals in the eastern Pacific. Proc Biol Sci. 2004;271:1757–63.
Post DM, Layman CA, Arrington DA, Takimoto G, Quattrochi J, Montaña CG. Getting to the fat of the matter: models, methods and assumptions for dealing with lipids in stable isotope analyses. Oecologia. 2007;152:179–89.
DeNiro MJ, Epstein S. Influence of diet on the distribution of carbon isotopes in animals. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. 1978;42:495–506.
Weisz JB. Measuring impacts of associated microbial communities on Caribbean reef sponges: searching for symbiosis. North Carolina, USA: University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill; 2006.
Mateo MA, Serrano O, Serrano L, Michener RH. Effects of sample preparation on stable isotope ratios of carbon and nitrogen in marine invertebrates: implications for food web studies using stable isotopes. Oecologia. 2008;157:105–15.
Knowlton N, Jackson JBC. New taxonomy and niche partitioning on coral reefs: Jack of all trades or master of some? Trends Ecol Evol. 1994;9:7–9.
Joy JB. Symbiosis catalyses niche expansion and diversification. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci. 2013;280:20122820.
Source: Ecology - nature.com


