Lockwood, J. L., Hoopes, M. F. & Marchetti, M. P. Invasion Ecology, https://doi.org/10.1111/aec.12295 (Wiley‐Blackwell, 2013).
Blackburn, T. M. et al. A unified classification of alien species based on the magnitude of their environmental impacts. PLoS Biol. 12 (2014).
Kolar, C. S. & Lodge, D. M. Progress in invasion biology: predicting invaders. Trends Ecol. Evol. 16, 199–204 (2001).
Simberloff, D. & Gibbons, L. Now you see them, now you don’t! – Population crashes of established introduced species. Biol. Invasions 6, 161–172 (2004).
Strayer, D. L. et al. Boom-bust dynamics in biological invasions: towards an improved application of the concept. Ecol. Lett. 20, 1337–1350 (2017).
Nei, M., Maruyama, T. & Chakraborty, R. The genetic bottleneck effect and genetic variability in populations. Evolution (N. Y). 29, 1–10 (1975).
Zhan, A. et al. Complex genetic patterns in closely related colonizing invasive species. Ecol. Evol. 2, 1331–1346 (2012).
Lee, K. A. & Klasing, K. C. A role for immunology in invasion biology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 19, 523–529 (2004).
Lambrinos, J. G. How interactions between ecology and evolution influence contemporary invasion dynamics. Ecology 85, 2061–2070 (2004).
Lee, C. E. Evolutionary genetics of invasive species. Trends Ecol. Evol. 17, 386–391 (2002).
Peake, J. et al. Feeding ecology of invasive lionfish (Pterois volitans and Pterois miles) in the temperate and tropical western Atlantic. Biol. Invasions 20, 2567–2597 (2018).
Rojas-Vélez, S., Tavera, J. & Acero, A. Unraveling lionfish invasion: is Pterois volitans truly a morphologically novel predator in the Caribbean? Biol. Invasions 21, 1921–1931 (2019).
Barker, B. D., Horodysky, A. Z. & Kerstetter, D. W. Hot or not? Comparative behavioral thermoregulation, critical temperature regimes, and thermal tolerances of the invasive lionfish Pterois sp. versus native western North Atlantic reef fishes. Biol. Invasions 20, 45–58 (2018).
Jud, Z. R., Nichols, P. K. & Layman, C. A. Broad salinity tolerance in the invasive lionfish Pterois spp. may facilitate estuarine colonization. Environ. Biol. Fishes 98, 135–143 (2015).
Fogg, A. Q. et al. Comparison of age and growth parameters of invasive red lionfish (Pterois volitans) across the northern Gulf of Mexico. Fish. Bull. 117, 1–15 (2019).
Gardner, P. G., Frazer, T. K., Jacoby, C. A. & Yanong, R. P. E. Reproductive biology of invasive lionfish (Pterois spp.). Front. Mar. Sci. 2, 7 (2015).
Fogg, A., Brown-Peterson, N. & Peterson, M. Reproductive life history characteristics of invasive red lionfish (Pterois volitans) in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Bull. Mar. Sci. 93, 791–813 (2017).
Green, S. J. & Côté, I. M. Record densities of Indo-Pacific lionfish on Bahamian coral reefs. Coral Reefs 28, 107–107 (2009).
Dahl, K., Edwards, M. & Patterson, W. F. III Density-dependent condition and growth of invasive lionfish in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 623, 145–159 (2019).
Côté, I. M. & Smith, N. S. The lionfish Pterois sp. invasion: has the worst-case scenario come to pass? J. Fish Biol. 92, 660–689 (2018).
Hixon, M., Green, S., Albins, M., Akins, J. & Morris, J. Lionfish: a major marine invasion. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 558, 161–165 (2016).
Dahl, K. A., Patterson, W. F. III. & Snyder, R. A. Experimental assessment of lionfish removals to mitigate reef fish community shifts on northern Gulf of Mexico artificial reefs. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 558, 207–221 (2016).
Albins, M. Invasive Pacific lionfish Pterois volitans reduce abundance and species richness of native Bahamian coral-reef fishes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 522, 231–243 (2015).
Green, S. J., Akins, J. L., Maljković, A. & Côté, I. M. Invasive lionfish drive Atlantic coral reef fish declines. PLoS One 7, e32596 (2012).
Lesser, M. P. & Slattery, M. Phase shift to algal dominated communities at mesophotic depths associated with lionfish (Pterois volitans) invasion on a Bahamian coral reef. Biol. Invasions 13, 1855–1868 (2011).
Kindinger, T. L. & Albins, M. A. Consumptive and non-consumptive effects of an invasive marine predator on native coral-reef herbivores. Biol. Invasions 19, (2017).
Chagaris, D. et al. An ecosystem-based approach to evaluating impacts and management of invasive lionfish. Fisheries 42, 421–431 (2017).
Kulbicki, M. et al. Distributions of Indo-Pacific lionfishes Pterois spp. in their native ranges: implications for the Atlantic invasion. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 446, 189–205 (2012).
Darling, E. S., Green, S. J., O’Leary, J. K. & Côté, I. M. Indo-Pacific lionfish are larger and more abundant on invaded reefs: A comparison of Kenyan and Bahamian lionfish populations. Biol. Invasions 13, 2045–2051 (2011).
Benkwitt, C. E. et al. Is the lionfish invasion waning? Evidence from The Bahamas. Coral Reefs 36, 1255–1261 (2017).
Hackerott, S. et al. Native predators do not influence invasion success of Pacific lionfish on Caribbean reefs. PLoS One 8, e68259 (2013).
Bejarano, S., Lohr, K., Hamilton, S. & Manfrino, C. Relationships of invasive lionfish with topographic complexity, groupers, and native prey fishes in Little Cayman. Mar. Biol. 162, 253–266 (2015).
Valdivia, A., Bruno, J. F., Cox, C. E., Hackerott, S. & Green, S. J. Re-examining the relationship between invasive lionfish and native grouper in the Caribbean. PeerJ 2, e348 (2014).
Anton, A., Simpson, M. S. & Vu, I. Environmental and biotic correlates to lionfish invasion success in Bahamian coral reefs. PLoS One 9, e106229 (2014).
Fogg, A. Q., Ruiz, C. F., Curran, S. S. & Bullard, S. A. Parasites from the red lionfish, Pterois volitans from the Gulf of Mexico. Gulf Caribb. Res. 27, SC 1-5 (2016).
Sellers, A. J., Ruiz, G. M., Leung, B. & Torchin, M. E. Regional variation in parasite species richness and abundance in the introduced range of the invasive lionfish, Pterois volitans. PLoS One 10, e0131075 (2015).
Tuttle, L. J., Sikkel, P. C., Cure, K. & Hixon, M. A. Parasite-mediated enemy release and low biotic resistance may facilitate invasion of Atlantic coral reefs by Pacific red lionfish (Pterois volitans). Biol. Invasions 19, 563–575 (2017).
Sikkel, P. C., Tuttle, L. J., Cure, K., Coile, A. M. & Hixon, M. A. Low susceptibility of invasive red lionfish (Pterois volitans) to a generalist ectoparasite in both its introduced and native ranges. PLoS One 9, e95854 (2014).
Loerch, S. M., McCammon, A. M. & Sikkel, P. C. Low susceptibility of invasive Indo-Pacific lionfish Pterois volitans to ectoparasitic Neobenedenia in the eastern Caribbean. Environ. Biol. Fishes 98, 1979–1985 (2015).
Benkwitt, C. E. Non-linear effects of invasive lionfish density on native coral-reef fish communities. Biol. Invasions 17, 1383–1395 (2015).
Benkwitt, C. Invasive lionfish increase activity and foraging movements at greater local densities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 558, 255–266 (2016).
Ingeman, K. E. Lionfish cause increased mortality rates and drive local extirpation of native prey. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 558, (2016).
Dahl, K. A. et al. Genotyping confirms significant cannibalism in northern Gulf of Mexico invasive red lionfish, Pterois volitans. Biol. Invasions 20, 3513–3526 (2018).
Benkwitt, C. E. Density-dependent growth in invasive lionfish (Pterois volitans). PLoS One 8, e66995 (2013).
Pérez-Portela, R. et al. Genetic homogeneity of the invasive lionfish across the Northwestern Atlantic and the Gulf of Mexico based on single nucleotide polymorphisms. Sci. Rep. 8, 5062 (2018).
Burford Reiskind, M. O. et al. The genomics of invasion: characterization of red lionfish (Pterois volitans) populations from the native and introduced ranges. Biol. Invasions 1–13, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-019-01992-0 (2019).
Johnson, J., Bird, C. E., Johnston, M. A., Fogg, A. Q. & Hogan, J. D. Regional genetic structure and genetic founder effects in the invasive lionfish: comparing the Gulf of Mexico, Caribbean and North Atlantic. Mar. Biol. 163, 216 (2016).
White, T. A. & Perkins, S. E. The ecoimmunology of invasive species. Funct. Ecol. 26, 1313–1323 (2012).
Harris, H. E. et al. First report of an emerging ulcerative skin disease in invasive lionfish. UF/IFAS Ext. Electron. Data Inf. Source FA209, 1–7 (2018).
Ahasan, M. S. et al. Determining the etiology of an emerging ulcerative disease in invasive lionfish. In 8th International Symposium on Aquatic Animal Health, https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.26050.63680 (2018).
Harris, H. E., Patterson, W. F. III., Ahrens, R. N. M. & Allen, M. S. Detection and removal efficiency of invasive lionfish in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Fish. Res. 213, 22–32 (2019).
Dahl, K. A. & Patterson, W. F. Habitat-specific density and diet of rapidly expanding invasive red lionfish, Pterois volitans, populations in the northern Gulf of Mexico. PLoS One 9, e105852 (2014).
Karnauskas, M. et al. Red snapper distribution on natural habitats and artificial structures in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Coast. Fish. 9, 50–67 (2017).
Johnson, E. G. & Swenarton, M. K. Age, growth and population structure of invasive lionfish (Pterois volitans/miles) in northeast Florida using a length-based, age-structured population model. PeerJ 4, e2730 (2016).
Barbour, A. B., Allen, M. S., Frazer, T. K. & Sherman, K. D. Evaluating the potential efficacy of invasive lionfish (Pterois volitans) removals. PLoS One 6, (2011).
Morris, J. A., Shertzer, K. W. & Rice, J. A. A stage-based matrix population model of invasive lionfish with implications for control. Biol. Invasions 13, 7–12 (2011).
Ramsay, J. M., Watral, V., Schreck, C. B. & Kent, M. L. Pseudoloma neurophilia infections in zebrafish (Danio rerio): effects of stress on survival, growth, and reproduction. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 88, 69–84 (2009).
Ellis, R. & Faletti, M. Native grouper indirectly ameliorates the negative effects of invasive lionfish. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 558, 267–279 (2016).
Diller, J. L., Frazer, T. K. & Jacoby, C. A. Coping with the lionfish invasion: evidence that naïve, native predators can learn to help. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 455, 45–49 (2014).
Maljković, A., Van Leeuwen, T. E. & Cove, S. N. Predation on the invasive red lionfish, Pterois volitans (Pisces: Scorpaenidae), by native groupers in the Bahamas. Coral Reefs 27, 501–501 (2008).
Mumby, P. J., Harborne, A. R. & Brumbaugh, D. R. Grouper as a natural biocontrol of invasive lionfish. PLoS One 6, 2–5 (2011).
Green, S. J. et al. Linking removal targets to the ecological effects of invaders: a predictive model and field test. Ecol. Appl. 24, 1311–1322 (2014).
Harms-Tuohy, C., Appeldoorn, R. & Craig, M. The effectiveness of small-scale lionfish removals as a management strategy: effort, impacts and the response of native prey and piscivores. Manag. Biol. Invasions 9, 149–162 (2018).
Morris, J. A., Shertzer, K. W. & Rice, J. A. A stage-based matrix population model of invasive lionfish with implications for control. Biol. Invasions 13, 7–12 (2010).
Smith, N. S., Green, S. J., Akins, J. L., Miller, S. & Côté, I. M. Density-dependent colonization and natural disturbance limit the effectiveness of invasive lionfish culling efforts. Biol. Invasions 19, 2385–2399 (2017).
Johnston, M. W. & Purkis, S. J. Hurricanes accelerated the Florida-Bahamas lionfish invasion. Glob. Chang. Biol. 21, 2249–2260 (2015).
Johnston, M. & Purkis, S. A coordinated and sustained international strategy is required to turn the tide on the Atlantic lionfish invasion. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 533, 219–235 (2015).
Johnston, M. W., Bernard, A. M. & Shivji, M. S. Forecasting lionfish sources and sinks in the Atlantic: are Gulf of Mexico reef fisheries at risk? Coral Reefs 36, 169–181 (2017).
Stevens, J. L. & Olson, J. B. Invasive lionfish harbor a different external bacterial community than native Bahamian fishes. Coral Reefs 32, 1113–1121 (2013).
Stevens, J., Jackson, R. & Olson, J. Bacteria associated with lionfish (Pterois volitans/miles complex) exhibit antibacterial activity against known fish pathogens. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 558, 167–180 (2016).
Torchin, M. E., Lafferty, K. D., Dobson, A. P., McKenzie, V. J. & Kuris, A. M. Introduced species and their missing parasites. Nature 421, 628–630 (2003).
Torchin, M. E., Lafferty, K. D. & Kuris, A. M. Parasites and marine invasions. Parasitology 124, 137–151 (2002).
Blakeslee, A. M. H., Fowler, A. E. & Keogh, C. L. Marine invasions and parasite escape: updates and new perspectives. Adv. Mar. Biol. 66, 87–169 (2013).
Gendron, A. D., Marcogliese, D. J. & Thomas, M. Invasive species are less parasitized than native competitors, but for how long? The case of the round goby in the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence Basin. Biol. Invasions 14, 367–384 (2012).
Peiffer, F., Bejarano, S., Palavicini de Witte, G. & Wild, C. Ongoing removals of invasive lionfish in Honduras and their effect on native Caribbean prey fishes. PeerJ 5, e3818 (2017).
Klein, D. R. The introduction, increase, and crash of reindeer on St. Matthew Island. J. Wildl. Manage. 32, 350 (1968).
Kelly, D. W., Paterson, R. A., Townsend, C. R., Poulin, R. & Tompkins, D. M. Parasite spillback: a neglected concept in invasion ecology? Ecology 90, 2047–2056 (2009).
Ziskowski, J. J. et al. Disease in commercially valuable fish stocks in the Northwest Atlantic. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 18, 496–504 (1987).
Murawski, S. A., Hogarth, W. T., Peebles, E. B. & Barbeiri, L. Prevalence of external skin lesions and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon concentrations in Gulf of Mexico fishes, post-Deepwater. Horizon. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 143, 1084–1097 (2014).
Pace, M. L., Strayer, D. L., Fischer, D. & Malcom, H. M. Recovery of native zooplankton associated with increased mortality of an invasive mussel. Ecosphere 1 (2010).
Ratcliffe, F. N., Myers, K., Fennessy, B. V. & Calaby, J. H. Myxomatosis in Australia: a step towards the biological control of the rabbit. Nature 170, 7–11 (1952).
Mutze, G., Cooke, B. & Alexander, P. The initial impact of rabbit hemorrhagic disease on European rabbit populations in South Australia. J. Wildl. Dis. 34, 221–227 (1998).
Kerr, P. J. Myxomatosis in Australia and Europe: a model for emerging infectious diseases. Antiviral Res. 93, 387–415 (2012).
Mutze, G. et al. Recovery of South Australian rabbit populations from the impact of rabbit haemorrhagic disease. Wildl. Res. 41, 552 (2014).
Mutze, G., Bird, P., Cooke, B. & Henzell, R. Geographic and seasonal variation in the impact of rabbit haemorrhagic disease on European rabbits, Oryctolagus cuniculus, and rabbit damage in Australia. in Lagomorph Biology 279–293, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-72446-9_19 (Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2008).
Kitchens, L. L. et al. Occurrence of invasive lionfish (Pterois volitans) larvae in the northern Gulf of Mexico: characterization of dispersal pathways and spawning areas. Biol. Invasions 19, 1971–1979 (2017).
Frazer, T. K., Jacoby, C. A., Edwards, M. A., Barry, S. C. & Manfrino, C. M. Coping with the lionfish invasion: can targeted removals yield beneficial effects? Rev. Fish. Sci. 20, 185–191 (2012).
Ogle, D. H. Weight-Length Relationships. in Introductory Fisheries Analyses with R 131–152 (Chapman and Hall/CRC, 2019). doi:10.1201/9781315371986-7.
Le Cren, E. D. The length-weight relationship and seasonal cycle in gonad weight and condition in the Perch (Perca fluviatilis). J. Anim. Ecol. 20, 201 (1951).
Froese, R. Cube law, condition factor and weight-length relationships: history, meta-analysis and recommendations. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 22, 241–253 (2006).
Neumann, R. M. & Allen, M. S. Size Structure. In Analysis and Interpretation of Freshwater Fisheries Data (eds. Guy, C. S. & Brown, M. L.) (American Fisheries Society, 2007).
Bolker, B. M. et al. Generalized linear mixed models: a practical guide for ecology and evolution. Trends Ecol. Evol. 24, 127–135 (2009).
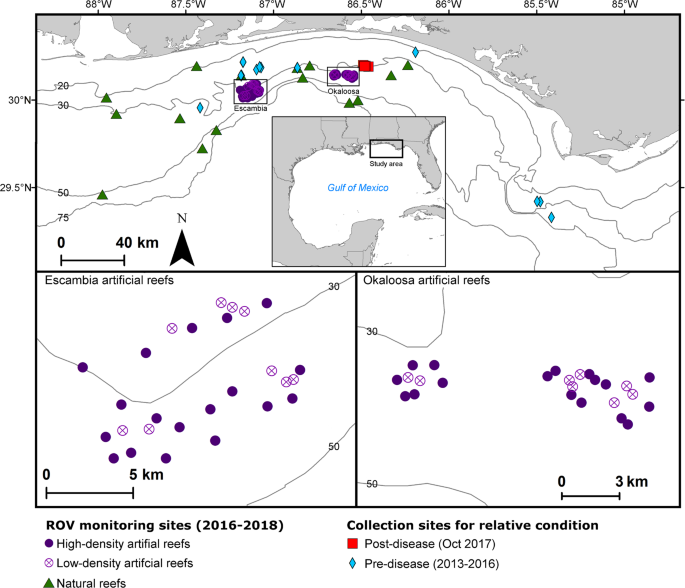
Patterson, W. F. III., Dance, M. A. & Addis, D. T. Development of a remotely operated vehicle based methodology to estimate fish community structure at artificial reef sites in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Proc. 61st Gulf Caibb. Fish. Inst. 263–270 (2009).
Patterson, W. F. III., Tarnecki, J. H., Addis, D. T. & Barbieri, L. R. Reef fish community structure at natural versus artificial reefs in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Proc. 66th Gulf Caribb. Fish. Inst. 4–8 (2013).
Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission. 2010–2018 commercial fishery landings data through batch 1402, https://myfwc.com/research/saltwater/fishstats/commercial-fisheries/landings-in-florida/ (2019).
Source: Ecology - nature.com


