Larson, G. et al. Current perspectives and the future of domestication studies. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 111, 6139–6146 (2014).
Barton, L. et al. Agricultural origins and the isotopic identity of domestication in northern China. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 106, 5523–5528 (2009).
Bettinger, R. L., Barton, L. & Morgan, C. T. The origins of food production in North China: a different kind of agricultural revolution. Evolutionary Anthropology 19, 9–21 (2010).
Bar-Yosef, O. Climatic fluctuations and early farming in West and East Asia. Current Anthropology 52, S175–S193 (2011).
Yan, W. Nong ye fa sheng yu wen ming qi yuan (The origin of agriculture and civilization). (Kexue Chubanshe (Science Press), 2000).
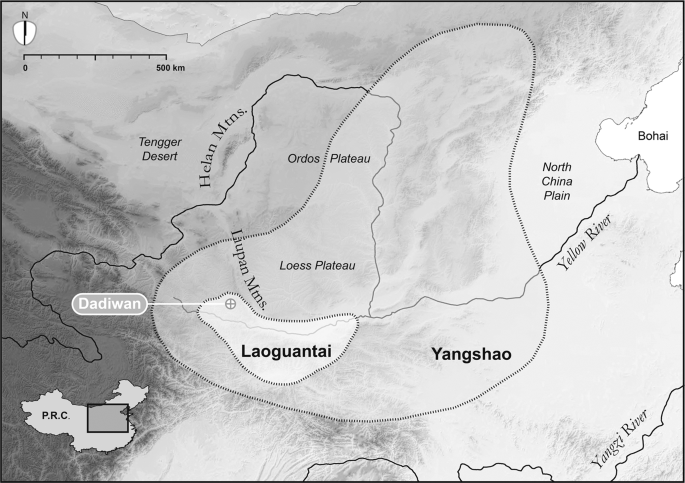
Barton, L. Early Food Production in China’s Western Loess Plateau, University of California, Davis, (2009).
Xiang, H. et al. Early Holocene chicken domestication in northern China. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 111, 17564–17569 (2014).
Peters, J. et al. Questioning new answers regarding Holocene chicken domestication in China. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 112, E2415 (2015).
Eda, M. et al. Reevaluation of early Holocene chicken domestication in northern China. Journal of Archaeological Science 67, 25–31 (2016).
Peng, M. S., Shi, N. N., Yao, Y. G. & Zhang, Y. P. Caveats about interpretation of ancient chicken mtDNAs from northern China. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 112, E1970–E1971 (2015).
Bennett, C. E. et al. The broiler chicken as a signal of a human reconfigured biosphere. Royal Society Open Science 5, 180325 (2018).
Peters, J., Lebrasseur, O., Deng, H. & Larson, G. Holocene cultural history of Red jungle fowl (Gallus gallus) and its domestic descendant in East Asia. Quaternary Science Reviews 142, 102–119 (2016).
Zhang, D. J. et al. Gansu Dadiwan yizhi jujin liuwannian lai de kaogu jilu yu hanzuo nongye qiyuan (Archaeological records of Dadiwan in the past 60 ka and the origin of millet agriculture). Zhongguo Kexue Yuan (Chinese Science Bulletin) 55, 887–894 (2010).
Bettinger, R. L. et al. In Late Quaternary Climate Change and Human Adaptation in Arid China Developments in Quaternary Science (Eds David B. Madsen, Xing Gao, & Fa Hu Chen) 83–101 (Elsevier, 2007).
GPICRA. (Gansu Provincial Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology) Qin’an Dadiwan xinshiqi shi dai yizhi fa jue baogao (Dadiwan in Qin’an: report on excavations at a Neolithic site). (Cultural Relics Publishing House, 2006).
Bettinger, R. L. et al. The transition to agriculture at Dadiwan, People’s Republic of China. Current Anthropology 51, 703–714 (2010).
Jensen, P. M., Madsen, P., Jensen, L. S. & Pipper, C. B. Differences in carbon and nitrogen stable isotope signatures amongst wild and released pheasant populations. European Journal of Wildlife Research 58, 755–760 (2012).
Lipe, W. D. et al. Cultural and genetic contexts for early turkey domestication in the northern Southwest. American Antiquity 81, 97–113 (2016).
Kozyrenko, M. M., Fisenko, P. V. & Zhuravlev, L. Genetic variation of Manchurian pheasant (Phasianus colchicus pallasi Rotshild, 1903) inferred from mitochondrial DNA control region sequences. Genetika 45 (2009).
Liu, Y., Zhan, X., Wang, N., Chang, J. & Zhang, Z. Effect of geological vicariance on mitochondrial DNA differentiation in Common Pheasant populations of the Loess Plateau and eastern China. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 55, 409–417 (2010).
Qu, J., Zhang, J. & Liu, N. Ecological genetics of Strauch’s Pheasant (Phasianus colchicus strauchi): correlation between environmental factors and population genetic variability. Genbank unpublished (2008).
Xu, X. L., Fu, Y., Wang, Y. & Bai, S. Y. Genetic divergence in northeast subspecies of the ring-necked pheasant. Genbank unpublished (2013).
Zhao, C., Liu, Z., Sun, Y. & Gao, H. Phasianus colchicus alaschanicus isolate HLSHJZ16688 mitochondrion, complete genome. Genbank unpublished (2015).
Leigh, J. W. & Bryant, D. PopART: full-feature softwared for haplotype network construction. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 6, 1110–1116 (2015).
Edgar, R. C. MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Research 32, 1792–1797 (2004).
Fourment, M. & Holmes, E. C. Segotron: a user-friendly sequence editor for Mac OS X. BMC Research Notes 9, 106 (2016).
Schwarz, G. Estimating the dimensions of a model. Annals of Statistics 6, 461–464 (1978).
Darriba, D., Taboada, G. L., Doallo, R. & Posada, D. j. ModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and high performance computing. Nature Methods 9, 772 (2012).
PAUP*. Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and other methods) (Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, 2003).
Hasegawa, M., Kishino, H. & Yano, T. Dating of the Human-Ape Splitting by a Molecular Clock of Mitochondrial DNA. Journal of Molecular Evolution 22, 160–74 (1985).
Kato, S., Nishibori, M. & Yasue, H. Pheasant complete mitochondrial genome. Genbank unpublished (2004).
Bouckaert, R. et al. BEAST 2.5: An advanced software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Computational Biology 15, e1006650 (2019).
Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30, 1312–1313 (2014).
Dabney, J., Meyer, M. & Paabo, S. Ancient DNA damage. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology 5, a012567 (2013).
Jonsson, H., Ginolhac, A., Schubert, M., Johnson, P. L. & Orlando, L. mapDamage2.0: fast approximate Bayesian estimates of ancient DNA damage parameters. Bioinformatics 29, 1682–1684 (2013).
Rohland, N., Harney, E., Mallick, S., Nordenfelt, S. & Reich, D. Partial uracil-DNA-glycosylase treatment for screening of ancient DNA. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B 3370, 20130624 (2015).
Neparaczki, E. et al. Revising mtDNA haplotypes of the ancient Hungarian conquerors with next generation sequencing. PLoS ONE 12, e0174886 (2017).
Kayvanfar, N., Aliabadian, M., Niu, X., Zhang, Z. & Liu, Y. Phylogeography of the common pheasant Phasianus colchicus. Ibis 159, 430–442 (2017).
Smith, B. D. Low-level food production. Journal of Archaeological Research 9, 1–43 (2001).
Atahan, P. et al. Subsistence and the isotopic signature of herding in the Bronze Age Hexi Corridor, NW Gansu, China. Journal of Archaeological Science 38, 1747–1753 (2011).
Chen, X. L. et al. Raising practices of Neolithic livestock evidenced by stable isotope analysis in the Wei River Valley, North China. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, https://doi.org/10.1002/oa.2393 (2014).
Dai, L., Kan, X. & Zhang, X. An investigation into the strategy of pig husbandry combining zooarchaeological and stable isotopic approaches at Neolithic Houjiazhai, China. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, https://doi.org/10.1002/oa.2788 (2019).
Source: Ecology - nature.com


