Muehlenbachs, K. The oxygen isotopic composition of the oceans, sediments and the seafloor. Chem. Geol. 145, 263–273 (1998).
Prokoph, A., Shields, G. & Veizer, J. Compilation and time-series analysis of a marine carbonate δ 18O, δ 13C, 87Sr/86Sr and δ 34S database through Earth history. Earth Sci. Rev. 87, 113–133 (2008).
Muehlenbachs, K. & Clayton, R. Oxygen isotope composition of the oceanic crust and its bearing on seawater. J. Geophys. Res. 81, 4365–4369 (1976).
Chase, C. & Perry, E. C. The oceans: growth and oxygen isotope evolution. Science 177, 992–994 (1973).
Knauth, L. P. & Lowe, D. R. High Archean climatic temperature inferred from oxygen isotope geochemistry of cherts in the 3.5 Ga Swaziland Supergroup, South Africa. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 115, 566–580 (2003).
Jaffrés, J. B., Shields, G. A. & Wallmann, K. The oxygen isotope evolution of seawater: a critical review of a long-standing controversy and an improved geological water cycle model for the past 3.4 billion years. Earth Sci. Rev. 83, 83–122 (2007).
Galili, N. et al. The geologic history of seawater oxygen isotopes from marine iron oxides. Science 365, 469–473 (2019).
Garcia, A. K., Schopf, J. W., Yokobori, S.-i, Akanuma, S. & Yamagishi, A. Reconstructed ancestral enzymes suggest long-term cooling of Earth’s photic zone since the Archean. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114, 4619–4624 (2017).
Kasting, J. F. et al. Paleoclimates, ocean depth, and the oxygen isotopic composition of seawater. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 252, 82–93 (2006).
Veizer, J. & Prokoph, A. Temperatures and oxygen isotopic composition of Phanerozoic oceans. Earth Sci. Rev. 146, 92–104 (2015).
Muehlenbachs, K. & Clayton, R. N. Oxygen isotope studies of fresh and weathered submarine basalts. Can. J. Earth Sci. 9, 172–184 (1972).
Muehlenbachs, K., Furnes, H., Fonneland, H. C. & Hellevang, B. Ophiolites as faithful records of the oxygen isotope ratio of ancient seawater: the Solund-Stavfjord Ophiolite Complex as a Late Ordovician example. Ophiolites Earth Hist. 218, 401–414 (2003).
Gregory, R. T. & Taylor, H. P. Jr An oxygen isotope profile in a section of Cretaceous oceanic crust, Samail Ophiolite, Oman: evidence for δ 18O buffering of the oceans by deep (>5 km) seawater-hydrothermal circulation at mid-ocean ridges. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 86, 2737–2755 (1981).
Gregory, R. T. in Ophiolites in Earth History Vol. 218 (eds Dilek, Y. & Robinson, P. T.) 353–368 (Geological Society, 2003).
Turchyn, A. V. et al. Reconstructing the oxygen isotope composition of late Cambrian and Cretaceous hydrothermal vent fluid. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 123, 440–458 (2013).
Hodel, F. et al. Fossil black smoker yields oxygen isotopic composition of neoproterozoic seawater. Nat. Commun. 9, 1453 (2018).
DePaolo, D. J. Isotopic effects in fracture-dominated reactive fluid–rock systems. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 70, 1077–1096 (2006).
Norton, D. & Taylor, H. Jr Quantitative simulation of the hydrothermal systems of crystallizing magmas on the basis of transport theory and oxygen isotope data: an analysis of the Skaergaard intrusion. J. Petrol. 20, 421–486 (1979).
Wunsch, C. The Ocean Circulation Inverse Problem (Cambridge Univ. Press, 1996).
Wing, B. A. & Ferry, J. M. Three-dimensional geometry of metamorphic fluid flow during Barrovian regional metamorphism from an inversion of combined petrologic and stable isotopic data. Geology 30, 639–642 (2002).
Wing, B. A. & Ferry, J. M. Magnitude and geometry of reactive fluid flow from direct inversion of spatial patterns of geochemical alteration. Am. J. Sci. 307, 793–832 (2007).
Taylor, H. P. Water/rock interactions and the origin of H2O in granitic batholiths: thirtieth William Smith lecture. J. Geolog. Soc. 133, 509–558 (1977).
Cathles, L. M. in The Kuroko and Related Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Deposits Vol. 5 (eds Ohmoto, H. & Skinner, B. J.) 439–487 (Economic Geology Publishing, 1983).
Taylor, H. P. Jr & Forester, R. W. An oxygen and hydrogen isotope study of the Skaergaard intrusion and its country rocks: a description of a 55-M.Y. old fossil hydrothermal system. J. Petrol. 20, 355–419 (1979).
Gillis, K. M., Muehlenbachs, K., Stewart, M., Gleeson, T. & Karson, J. Fluid flow patterns in fast spreading East Pacific Rise crust exposed at Hess Deep. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 106, 26311–26329 (2001).
Green, G. R., Ohmoto, H., Date, J. & Takahashi, T. in The Kuroko and Related Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Deposits Vol. 5 (eds Ohmoto, H. & Skinner, B. J.) 395–411 (Economic Geology Publishing, 1983).
Schiffman, P. & Smith, B. M. Petrology and oxygen isotope geochemistry of a fossil seawater hydrothermal system within the Solea graben, northern Troodos ophiolite, Cyprus. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 93, 4612–4624 (1988).
Mukasa, S. B. & Ludden, J. N. Uranium-lead isotopic ages of plagiogranites from the Troodos ophiolite, Cyprus, and their tectonic significance. Geology 15, 825–828 (1987).
Lear, C., Elderfield, H. & Wilson, P. Cenozoic deep-sea temperatures and global ice volumes from Mg/Ca in benthic foraminiferal calcite. Science 287, 269–272 (2000).
Vearncombe, S. et al. 3.26 Ga black smoker-type mineralization in the Strelley Belt, Pilbara Craton, Western Australia. J. Geol. Soc. 152, 587–590 (1995).
Brauhart, C. W., Groves, D. I. & Morant, P. Regional alteration systems associated with volcanogenic massive sulfide mineralization at Panorama, Pilbara, Western Australia. Econ. Geol. 93, 292–302 (1998).
Buick, R. et al. Geochronology and stratigraphic relationships of the Sulphur Springs Group and Strelley Granite: a temporally distinct igneous province in the Archaean Pilbara Craton, Australia. Precambrian Res. 114, 87–120 (2002).
Van Kranendonk, M. J. et al. Making it thick: a volcanic plateau origin of Palaeoarchean continental lithosphere of the Pilbara and Kaapvaal cratons. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 389, 83–111 (2015).
Kato, Y. & Nakamura, K. Origin and global tectonic significance of Early Archean cherts from the Marble Bar greenstone belt, Pilbara Craton, Western Australia. Precambrian Res. 125, 191–243 (2003).
Nijman, W., Kloppenburg, A. & de Vries, S. T. Archaean basin margin geology and crustal evolution: an East Pilbara traverse. J. Geol. Soc. 174, 1090–1112 (2017).
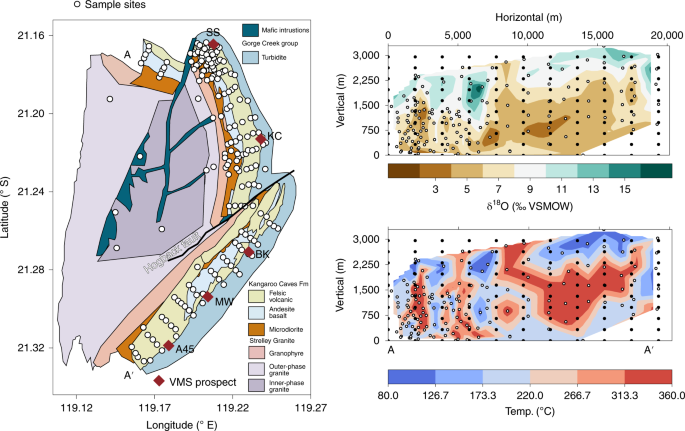
Martindale, J., Hagemann, S., Huston, D. & Danyushevsky, L. Integrated stratigraphic–structural–hydrothermal alteration and mineralisation model for the Kangaroo Caves zinc–copper deposit, Western Australia. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 61, 159–185 (2014).
Huston, D. L., Brauhart, C. W., Drieberg, S. L., Davidson, G. J. & Groves, D. I. Metal leaching and inorganic sulfate reduction in volcanic-hosted massive sulfide mineral systems: evidence from the paleo-Archean Panorama district Western Australia. Geology 29, 687–690 (2001).
Brauhart, C. W., Huston, D. L., Groves, D. I., Mikucki, E. J. & Gardoll, S. J. Geochemical mass-transfer patterns as indicators of the architecture of a complete volcanic-hosted massive sulfide hydrothermal alteration system, Panorama District, Pilbara, Western Australia. Econ. Geol. 96, 1263–1278 (2001).
Drieberg, S. L. et al. The interplay of evolved seawater and magmatic-hydrothermal fluids in the 3.24 Ga Panorama volcanic-hosted massive sulfide hydrothermal system, North Pilbara Craton, Western Australia. Econ. Geol. 108, 79–110 (2013).
Brauhart, C., Huston, D. & Andrew, A. Oxygen isotope mapping in the Panorama VMS district, Pilbara Craton, Western Australia: applications to estimating temperatures of alteration and to exploration. Mineral. Depos. 35, 727–740 (2000).
Pope, E. C., Bird, D. K. & Rosing, M. T. Isotope composition and volume of Earth’s early oceans. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 109, 4371–4376 (2012).
Silverman, S. R. The isotope geology of oxygen. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2, 26–42 (1951).
Gregory, R. T. in Stable Isotope Geochemistry: A tribute to Samuel Epstein Vol. 3 (eds Taylor, Jr., H. P., O’Neil, J. R. & Kaplan, I. R.) 65–76 (Geochemical Society, 1991).
Eiler, J. M. Oxygen isotope variations of basaltic lavas and upper mantle rocks. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 43, 319–364 (2001).
Lebrun, T. et al. Thermal evolution of an early magma ocean in interaction with the atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 118, 1155–1176 (2013).
Holland, H. D. The Chemical Evolution of the Atmosphere and Oceans (Princeton Univ. Press, 1984).
Korenaga, J. Initiation and evolution of plate tectonics on Earth: theories and observations. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 41, 117–151 (2013).
Buick, R. et al. Record of emergent continental crust ~3.5 billion years ago in the Pilbara craton of Australia. Nature 375, 574–577 (1995).
Grandstaff, D., Edelman, M., Foster, R., Zbinden, E. & Kimberley, M. Chemistry and mineralogy of Precambrian paleosols at the base of the Dominion and Pongola Groups (Transvaal, South Africa). Precambrian Res. 32, 97–131 (1986).
Bindeman, I., Bekker, A. & Zakharov, D. Oxygen isotope perspective on crustal evolution on early Earth: a record of Precambrian shales with emphasis on paleoproterozoic glaciations and great oxygenation event. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 437, 101–113 (2016).
Korenaga, J., Planavsky, N. J. & Evans, D. A. Global water cycle and the coevolution of the Earth as interior and surface environment. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 375, 20150393 (2017).
Taylor, S. R. & McLennan, S. M. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Rev. Geophys. 33, 241–265 (1995).
Simon, L. & Lècuyer, C. Continental recycling: the oxygen isotope point of view. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 6, Q08004 (2005).
Molnar, P. Gravitational potential energy per unit area as a constraint on Archean sea level. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 19, 4063–4095 (2018).
Cowan, N. B. & Abbot, D. S. Water cycling between ocean and mantle: super-earths need not be waterworlds. Astrophys. J. 781, 27 (2014).
Laverne, C., Agrinier, P., Hermitte, D. & Bohn, M. Chemical fluxes during hydrothermal alteration of a 1200-m long section of dikes in the oceanic crust, DSDP/ODP Hole 504B. Chem. Geol. 181, 73–98 (2001).
Cole, D. R., Mottl, M. J. & Ohmoto, H. Isotopic exchange in mineral–fluid systems. II. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopic investigation of the experimental basalt–seawater system. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 51, 1523–1538 (1987).
Stakes, D. S. & Taylor, H. P. in Ophiolites in Earth History Vol. 218 (eds Dilek, Y. & Robinson, P. T.) 315–351 (Geological Society, 2003).
Wanless, V. et al. Volatile abundances and oxygen isotopes in basaltic to dacitic lavas on mid-ocean ridges: the role of assimilation at spreading centers. Chem. Geol. 287, 54–65 (2011).
Grimes, C. B., Ushikubo, T., Kozdon, R. & Valley, J. W. Perspectives on the origin of plagiogranite in ophiolites from oxygen isotopes in zircon. Lithos 179, 48–66 (2013).
Source: Ecology - nature.com


