Monnin, E. et al. Atmospheric CO2 concentrations over the last glacial termination. Science 291, 112–114 (2001).
Toggweiler, J. Variation of atmospheric CO2 by ventilation of the ocean’s deepest water. Paleoceanography, 14. (1999).
Jacobel, A. W. et al. Repeated storage of respired carbon in the equatorial Pacific Ocean over the last three glacial cycles. Nat. Commun. 8, 1727 (2017).
Talley, L. D. Closure of the global overturning circulation through the Indian, Pacific and Southern Oceans: schematics and transports. Oceanography 26, 80–97 (2013).
Skinner, L. C. et al. Ventilation of the deep Southern Ocean and deglacial CO2 rise. Science 328, 1147–1151 (2010).
Burke, A. & Robinson, L. F. The Southern Ocean’s role in carbon exchange during the last deglaciation. Science 335, 557–561 (2012).
Siani, G. et al. Carbon isotope records reveal precise timing of enhanced Southern Ocean upwelling during the last deglaciation. Nat. Commun. 4, 2758 (2013).
Rae, J. W. et al. CO2 storage and release in the deep Southern Ocean on millennial to centennial timescales. Nature 592, 569–573 (2018).
Sarmiento, J. L. et al. High-latitude controls of thermocline nutrients and low latitude biological productivity. Nature 427, 56–60 (2004).
Moore, J. K. et al. Sustained climate warming drives declining marine biological productivity. Science 359, 1139–1143 (2018).
Skinner, L. C. & Shackleton, N. J. An Atlantic lead over Pacific deep-water change across Termination I: implications for the application of the marine isotope stage stratigraphy. Quat. Sci. Rev. 24, 571–580 (2005).
Lisiecki, L. E. & Raymo, M. E. Diachronous benthic δ18O responses during late Pleistocene terminations. Paleoceanography 24, 1–14 (2009).
Stern, J. V. & Lisiecki, L. E. Termination 1 timing in radiocarbon-dated regional benthic δ18O stacks. Paleoceanography 29, 1127–1142 (2014).
Sikes, E. L., Allen, K. A. & Lund, D. C. Enhanced δ13C and δ18O differences between the South Atlantic and South Pacific during the last glaciation: the deep gateway hypothesis. Paleoceanography 32, 1000–1017 (2017).
Zhao, N. et al. A synthesis of deglacial deep-sea radiocarbon records and their (In)consistency with modern Ocean ventilation. Paleoceanogr. Paleoclimatology 33, 128–151 (2018).
Bostock, H. C. et al. Carbon isotope evidence for changes in Antarctic Intermediate Water circulation and ocean ventilation in the southwest Pacific during the last deglaciation. Paleoceanography 19, 1–15 (2004).
Jaccard, S. L. & Galbraith, E. D. Direct ventilation of the North Pacific did not reach the deep ocean during the last deglaciation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 40, 199–203 (2013).
Sikes, E. L. et al. Glacial water mass structure and rapid δ18O and δ13C changes during the last glacial termination in the Southwest Pacific. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 456, 87–97 (2016).
Clementi, V. J. & Sikes, E. L. Southwest pacific vertical structure influences on Oceanic carbon storage since the last glacial maximum. Paleoceanogr. Paleoclimatology 34, 734–754 (2019).
Egge, J. & Aksnes, D. Silicate as regulating nutrient in phytoplankton competition. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 83, 281–289 (1992).
Dugdale, R. C. & Wilkerson, F. P. Silicate regulation of new production in the equatorial Pacific upwelling. Nature 391, 270–273 (1998).
Buesseler, K. The decoupling of production and particulate export in the surface ocean. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 12, 297–310 (1998).
Sigman, D. M. & Boyle, E. A. Glacial/interglacial variation in atmospheric carbon dioxide. Nature 407, 859–869 (2000).
Matsumoto, K. & Sarmiento, J. L. A corollary to the silicic acid leakage hypothesis. Paleoceanography 23, 2 (2008).
Ragueneau, O. et al. Si/C decoupling in the world ocean: Is the Southern Ocean different? Deep-Sea Res. Ii. 49, 3127–3154 (2002).
De La Rocha, C. L., Brzezinski, M. A. & DeNiro, M. J. Fractionation of silicon isotopes by marine diatoms during biogenic silica formation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 61, 5051–5056 (1997).
Egan, K. E. et al. Diatom silicon isotopes as a proxy for silicic acid utilisation: a Southern Ocean core top calibration. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 96, 174–192 (2012).
De La Rocha, C. L. et al. Silicon-isotope composition of diatoms as an indicator of diatoms as an indicator of past oceanic change. Nature 395, 28–31 (1998).
Hendry, K. R. & Robinson, L. F. The relationship between silicon isotope fractionation in sponges and silicic acid concentration: Modern and core-top studies of biogenic opal. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 81, 1–12 (2012).
Hendry, K. R. & Brzezinski, M. A. Using silicon isotopes to understand the role of the Southern Ocean in modern and ancient biogeochemistry and climate. Quat. Sci. Rev. 89, 13–26 (2014).
Cardinal, D. et al. Relevance of silicon isotopes to Si-nutrient utilization and Si-source assessment in Antarctic waters. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles. 19, GB2007 (2005).
Fripiat, F. et al. Silicon pool dynamics and biogenic silica export in the Southern Ocean inferred from Si-isotopes. Ocean Sci. 7, 533–547 (2011).
Beucher, C. P., Brzezinski, M. A. & Crosta, X. Silicic acid dynamics in the glacial sub-Antarctic: implications for the silicic acid leakage hypothesis. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 21, 1–13 (2007).
Horn, M. G. et al. Southern Ocean nitrogen and silicon dynamics during the last deglaciation. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 310, 334–339 (2011).
Robinson, R. S. et al. The changing roles of iron and vertical mixing in regulating nitrogen and silicon cycling in the Southern Ocean over the last glacial cycle. Paleoceanography 29, 1179–1195 (2014).
Brzezinski, M. A. et al. A switch from Si(OH)4 to NO3− depletion in the glacial Southern Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 29, 3–6 (2002).
Sutton, J. N. et al. Species-dependent silicon isotope fractionation by marine diatoms. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 104, 300–309 (2013).
Francois, R. et al. 230Th normalization: an essential tool for interpreting sedimentary fluxes during the late Quaternary. Paleoceanography 19, PA1018 (2004).
Dézileau, L., Reyss, J. L. & Lemoine, F. Late Quaternary changes in biogenic opal fluxes in the Southern Indian Ocean. Mar. Geol. 202, 143–158 (2003).
Lambert, F. et al. Dust-climate couplings over the past 800,000 years from the EPICA Dome C ice core. Nature 452, 616–619 (2008).
Martínez-García, A. et al. Iron fertilization of the Subantarctic ocean during the last ice age. Science 343, 1347–1350 (2014).
Fripiat, F. et al. Diatom-induced silicon isotopic fractionation in Antarctic sea ice. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 112, G02001 (2007).
Anderson, R. F. et al. Wind-driven upwelling in the Southern Ocean and the deglacial rise in atmospheric CO2. Science 323, 1443–1448 (2009).
Abelmann, A. et al. The seasonal sea-ice zone in the glacial Southern Ocean as a carbon sink. Nat. Commun. 6, 8136 (2015).
Hendry, K. R. et al. Abrupt changes in high-latitude nutrient supply to the Atlantic during the last glacial cycle. Geology 40, 123–126 (2012).
Meckler, A. N. et al. Deglacial pulses of deep-ocean silicate into the subtropical North Atlantic Ocean. Nature 495, 495–498 (2013).
Ellwood, M. J., Wille, M. & Maher, W. Glacial silicic acid concentrations in the Southern. Ocean. Sci. 330, 1088–1091 (2010).
Sarmiento, J. L. et al. Deep ocean biogeochemistry of silicic acid and nitrate. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 21, 1–16 (2007).
De Souza, G. F. et al. Silicon stable isotope distribution traces Southern Ocean export of Si to the eastern South Pacific thermocline. Biogeosci 9, 4199–4213 (2012).
Pichevin, L. E. et al. Enhanced carbon pump inferred from relaxation of nutrient limitation in the glacial ocean. Nature 459, 1114–1117 (2009).
Ronge, T. A. et al. Radiocarbon constraints on the extent and evolution of the South Pacific glacial carbon pool. Nat. Commun. 7, 1–12 (2016).
Du, J. et al. Flushing of the deep Pacific Ocean and the deglacial rise of atmospheric CO2 concentrations. Nat. Geosci. 11, 749–755 (2018).
Basak, C. et al. Breakup of last glacial deep stratification in the South Pacific. Science 359, 900–904 (2018).
Ferrari, R. et al. Antarctic sea ice control on ocean circulation in present and glacial climates. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 111, 8753–8758 (2014).
Curry, W. B. & Oppo, D. W. Glacial water mass geometry and the distribution of δ13C of ΣCO2 in the western Atlantic Ocean. Paleoceanography 20, 1–12 (2005).
Liu, W. et al. The de-correlation of westerly winds and westerly-wind stress over the Southern Ocean during the Last Glacial Maximum. Clim. Dyn. 45, 3157–3168 (2015).
Adkins, J. F. The role of deep ocean circulation in setting glacial climates. Paleoceanography 28, 539–561 (2013).
McCave, I. N., Carter, L. & Hall, I. R. Glacial-interglacial changes in water mass structure and flow in the SW Pacific Ocean. Quat. Sci. Rev. 27, 1886–1908 (2008).
Ferry, A. J. et al. First records of winter sea ice concentration in the southwest Pacific sector of the Southern Ocean. Paleoceanography 30, 1525–1539 (2015).
Pedro, J. B. et al. The spatial extent and dynamics of the Antarctic Cold Reversal. Nat. Geosci. 9, 51–55 (2015).
Xiao, W., Esper, O. & Gersonde, R. Last Glacial—Holocene climate variability in the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean. Quat. Sci. Rev. 135, 115–137 (2016).
Mayr, C. et al. Intensified Southern Hemisphere Westerlies regulated atmospheric CO2 during the last deglaciation. Geology 41, 831–834 (2013).
Jones, D. C. et al. Spatial and seasonal variability of the air-sea equilibration timescale of carbon dioxide. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 28, 1163–1178 (2014).
McManus, J. F. et al. Collapse and rapid resumption of Atlantic meridional circulation linked to deglacial climate changes. Nature 428, 834–837 (2004).
Barker, S. et al. Extreme deepening of the Atlantic overturning circulation during deglaciation. Nat. Geosci. 3, 567–571 (2010).
Ayers, J. M. & Strutton, P. G. Nutrient variability in Subantarctic Mode Waters forced by the Southern Annular Mode and ENSO. Geophys. Res. Lett. 40, 3419–3423 (2013).
Matsumoto, K., Sarmiento, J. L. & Brzezinski, M. A. Silicic acid leakage from the Southern Ocean: a possible explanation for glacial atmospheric pCO2. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 16, 1031 (2002).
Harrison, G. Role of increased marine silica input on paleo-pCO2 levels. Paleoceanography 15, 292–298 (2000).
Dugdale, R. C. et al. Influence of equatorial diatom processes on Si deposition and atmospheric CO2 cycles at glacial/interglacial timescales. Paleoceanography 19, PA3011 (2004).
Romero, O. et al. Oscillations of the siliceous imprint in the central Benguela Upwelling System from MIS 3 through to the early Holocene: the influence of the Southern Ocean. J. Quat. Sci. 18, 733–743 (2003).
Romero, O., Kim, J.-H. & Donner, B. Submillennial-to-millennial variability of diatom production off Mauritania, NW Africa, during the last glacial cycle. Paleoceanography, 23, PA3218 (2008).
Bradtmiller, L. I. et al. Opal burial in the equatorial Atlantic Ocean over the last 30 ka: Implications for glacial-interglacial changes in the ocean silicon cycle. Paleoceanography 22, PA4216 (2007).
Maier, E. et al. Deglacial subarctic Pacific surface water hydrography and nutrient dynamics and links to North Atlantic climate variability and atmospheric CO2. Paleoceanography 30, 949–968 (2015).
Hutchins, D. A. & Boyd, P. W. Marine phytoplankton and the changing ocean iron cycle. Nat. Clim. Change 6, 1072–1079 (2016).
Takeda, S. Influence of iron availability on nutrient consumption ratio of diatoms in oceanic waters. Nature 393, 774–777 (1998).
Bradtmiller, L. I. et al. Comparing glacial and Holocene opal fluxes in the Pacific sector of the Southern Ocean. Paleoceanography 24, 1–20 (2009).
Matsumoto, K., Chase, Z. & Kohfeld, K. Different mechanisms of silicic acid leakage and their biogeochemical consequences. Paleoceanography 29, 238–254 (2014).
Jochum, K. P. et al. Whole-Ocean changes in silica and Ge/Si ratios during the last deglacial deduced from long-lived giant glass sponges. Geophys. Res. Lett. 4, 11555–11564 (2017).
Frings, P. J. et al. The continental Si cycle and its impact on the ocean Si isotope budget. Chem. Geol. 425, 12–36 (2016).
Francois, R. et al. Contribution of Southern Ocean surface-water stratification to low atmospheric CO2 concentrations during the last glacial period. Nature 389, 929–935 (1997).
Chase, Z. et al. Accumulation of biogenic and lithogenic material in the Pacific sector of the Southern Ocean during the past 40,000 years. Deep Sea Res. II 50, 799–832 (2003).
Zhang, Y. G. et al. A 40-million-year history of A 40-million-year history of atmospheric CO2. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 371, 20130096 (2016).
Renaudie, J. Quantifying the Cenozoic marine diatom deposition history: links to the C and Si cycles. Biogeosciences 13, 6003–6014 (2016).
Morley, D. W. et al. Cleaning of lake sediment samples for diatom oxygen isotope analysis. J. Paleolimnol. 31, 391–401 (2004).
Georg, R. B. et al. New sample preparation techniques for the determination of Si isotopic compositions using MC-ICPMS. Chem. Geol. 235, 95–104 (2006).
Mortlock, R. & Froelich, P. A simple method for the rapid determination of biogenic opal in pelagic marine sediments. Deep Sea Res. A 36, 1415–1426 (1989).
Anderson, R. F. & Fleer, A. P. Determination of natural actinides and plutonium in marine particulate material. Anal. Chem. 54, 1142–1147 (1982).
Martínez-Garcia, A. et al. Links between iron supply, marine productivity, sea surface temperature, and CO2 over the last 1.1 Ma. Paleoceanography, 24. (2009).
Negre, C. et al. Separation and measurement of Pa, Th, and U isotopes in marine sediments by microwave-assisted digestion and multiple collector inductively coupled plasma mass. Anal. Chem. 81, 1914–1919 (2009).
Kretschmer, S. et al. Fractionation of 230Th, 231Pa, and 10Be induced by particle size and composition within an opal-rich sediment of the Atlantic Southern Ocean. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 75, 6971–6987 (2011).
Dumont, M. et al. Deglacial diatom and sponge silicon isotope records from cores MD84-551, MD88-773 and MD88-772. PANGAEA https://doi.pangaea.de/10.1594/PANGAEA.911189 (2020).
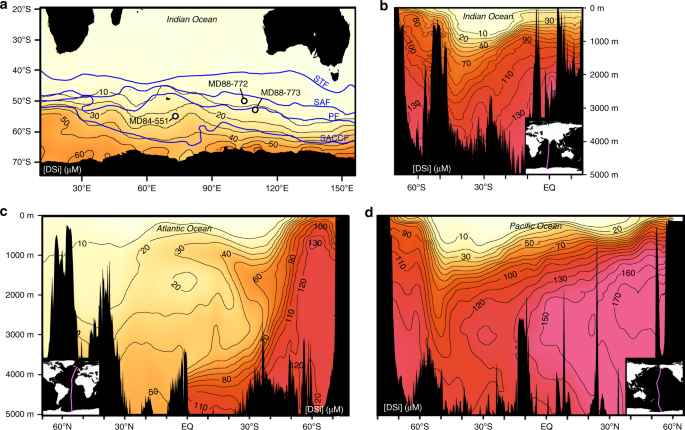
Orsi, A., Whitworth, T. & Nowlin, W. On the meridional extent and fronts of the Antarctic Circumpolar. Curr. Deep Sea Res. I 42, 641–673 (1995).
Garcia, H. E. et al.in World Ocean Atlas 2013, Volume 4: Dissolved Inorganic Nutrients (phosphate, nitrate, silicate). (eds Levitus, S., Mishonov, A. V.) (NOAA Atlas NESDIS 76, 2013).
Schlitzer, R. Interactive analysis and visualization of geoscience data with Ocean Data View. Comput. Geosci. 28, 1211–1218 (2002).
Rousseau, J. et al. Estimates of late Quaternary mode and intermediate water silicic acid concentration in the Pacific Southern Ocean. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 439, 101–108 (2016).
Source: Ecology - nature.com



